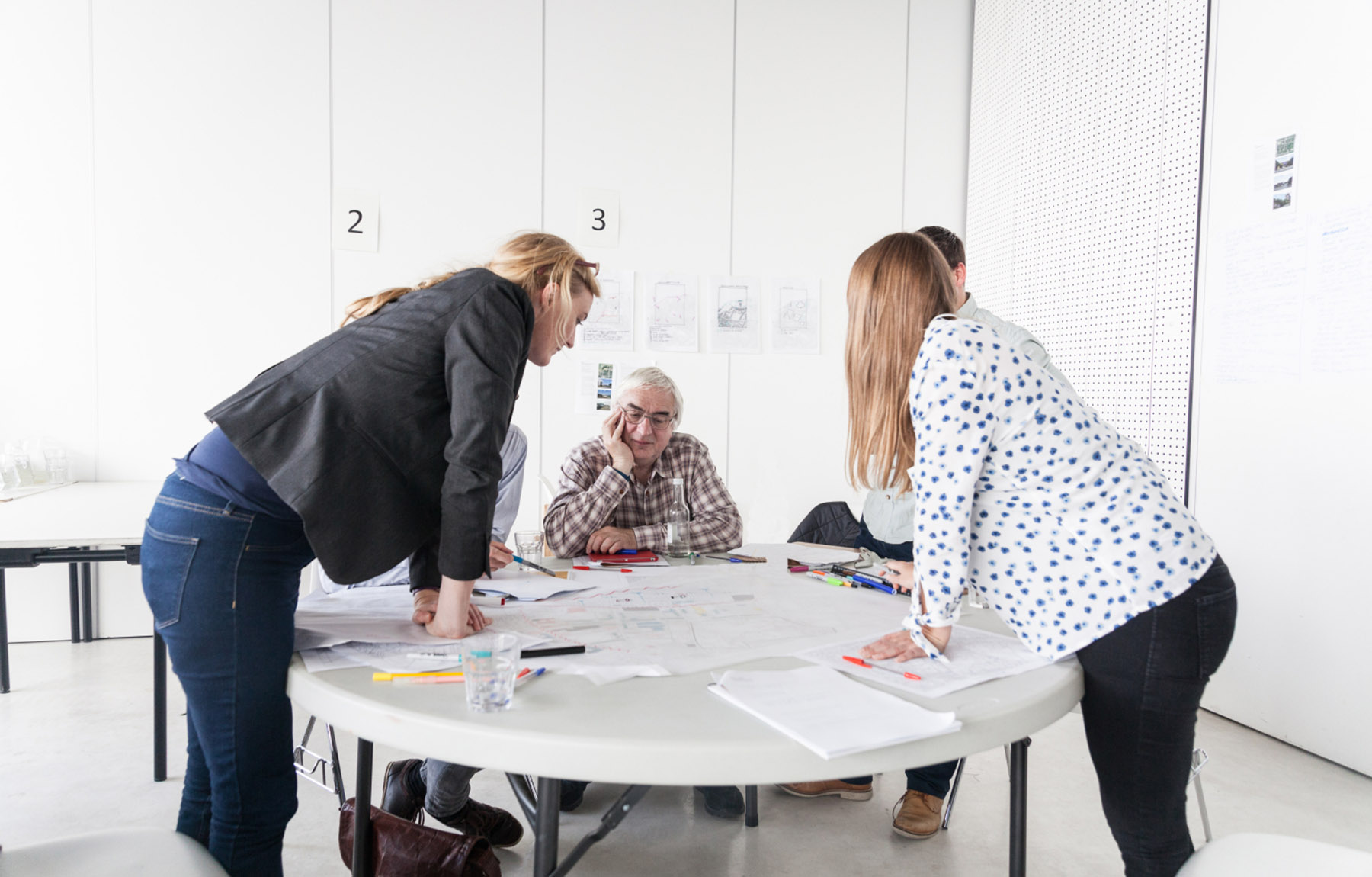
Professional Practice in Architecture (ARB/RIBA Part 3) at UCA
Complete the final stage in your training to become an architect with our Postgraduate Certificate in Professional Practice in Architecture (Part 3).
This 12-month course provides you with the foundation for life-long learning and development towards becoming a certified member of the architectural profession. It is predominantly taught online, allowing you the flexibility to manage your time appropriately around your professional practice commitments.
Programmed lectures will be uploaded throughout the course, and will remain available so you can watch and re-watch at your own pace, while programmed online webinars/tutorials will happen periodically at pre-determined times to encourage discourse around taught topics and the development of an online community.
This course will equip you with the skills and competencies you need to work in an ethical and professional manner. The content of the course is based on helping you to satisfy each of the professional competencies laid out jointly by the ARB/RIBA. Namely:
PC1 Professionalism
PC2 Clients, users, and delivery of services
PC3 Legal framework and processes
PC4 Practice and management
PC5 Building procurement
This course has received accreditation from ARB and RIBA
(Image above by www.kentdesign.org)
Accreditations, partners and industry connections
RIBA
The Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) is a global professional membership body and charity, driving excellence in architecture.

ARB
The Architects’ Registration Board (ARB) is an independent professional regulator, accountable to government. It ensures only those who are suitably competent are allowed to practice as architects.
What you'll
study
The content of the course may be subject to change. Curriculum content is provided as a guide.
The course runs for 12-months and is a part-time course.
The assessment comprises several elements for successful completion and are as follows:
- Legal Frameworks Online exam
- Architectural Practice Management Report
- Professional Case Study
- Oral Examination (taken in the final month of the course)
- Record of Professional Experience; evidence of 24 months’ professional experience, usually recorded in the form of a Professional Experience Development Record (PEDR)
- Career Appraisal, inclusive of your CV.
Practice and Entrepreneurship
The Practice and Entrepreneurship unit focuses upon the elements of the curriculum set out by the ARB/RIBA within the Professional Competencies (PC) 3 through to 5. It delivers teaching through an online lecture series and intensive tutorial/seminar days.
The teaching provided will augment and develop best practice approaches to areas already expected to have been encountered through your Professional Experience. As such, whilst the unit focus is on PCs 3, 4 & 5, some aspects of PCs 1 & 2 (relating to the professional role of the Architect) will also be outlined in lectures and included in assessment.
The following topics are considered as core content within the unit lecture series:
PC3 Legal framework and processes
1. The relevant UK legal systems, civil liabilities and the laws of contract and tort (delict)*
2. Planning and Conservation Acts, guidance and processes
3. Building regulations, approved documents and standards, guidance and processes
4. Land law, property law and rights of other proprietors
5. Terms within construction contracts implied by statute
6. Health and safety legislation and regulations
7. Statutory undertakers and authorities, their requirements and processes
8. Environmental and sustainability legislation
9. Historic buildings legislation
10. Accessibility and inclusion legislation
* Scotland
PC4 Practice and management
1. The roles of architectural practice in the construction industry
2. External factors affecting construction and practice at national and international levels
3. Practice structures, legal status and business styles
4. Personnel management and employment related legislation
5. Practice finance, business planning, funding and taxation
6. Marketing, fee calculation, bidding and negotiation
7. Resource management and job costing
8. Administration, quality management, QA systems, recording and review
9. Staff development, motivation, supervision and planning
10. Team working and leadership
PC5 Building procurement
1. Procurement methods, including for public and larger projects and relevant legislation
2. The effect of different procurement processes on programme, cost, risk and quality
3. Collaboration in construction and provisions for team working
4. Tendering methods, codes, procedures and project planning
5. Forms of contract and sub-contract, design responsibility and third party rights
6. Application and use of contract documentation;
7. Roles of design/construction team members and their interaction;
8. Duties and powers of a lead consultant and contract administrator;
9. Site processes, quality monitoring, progress recording, payment and completion;
10. Claims, litigation and alternative dispute resolution methods.
Professional Development and Reflection
The Professional Development and Reflection unit focuses upon the elements of the curriculum set out by the ARB/RIBA, within the Professional Competencies (PC) 1 and 2. It delivers teaching through an online lecture series and intensive tutorial/seminar days.
The teaching provided will augment and develop best practice approaches to areas already expected to be known and documented through your Professional Experience. As such, whilst the unit focus is on PCs 1 & 2, some aspects of PCs 3, 4 & 5 (previously taught in CARC 7201) will be revisited in lectures and included in assessment.
The following topics are considered as core content within the unit lecture series:
PC1 Professionalism
1. Professional ethics
2. The architect's obligation to society and the protection of the environment
3. Professional regulation, conduct and discipline
4. Institutional membership, benefits, obligations and codes of conduct
5. Attributes of integrity, impartiality, reliability and courtesy
6. Time management, recording, planning and review
7. Effective communication, presentation, confirmation and recording
8. Flexibility, adaptability and the principles of negotiation
9. Autonomous working and taking responsibility within a practice context
10. Continuing professional development.
PC2 Clients, users, and delivery of services
1. Types of clients, their priorities and the management of the relationship
2. Briefing, organising and the programming of services appropriate to appointment
3. Architects’ contracts, terms of engagement, scope of services and relevant legislation
4. Obligations to stakeholders, warranties and third party rights
5. Communication, progress reporting and the provision of appropriate and timely advice
6. Budget and financial awareness and cost monitoring or control
7. Responsibility for coordination and integration of design team input
8. Invoicing, payment of fees and financial management
9. Intellectual property rights and copyright law
10. Duty of care, professional liability, negligence and professional indemnity including insurance.
Course specifications
Please note, syllabus content indicated is provided as a guide. The content of the course may be subject to change in line with our Student Terms and Conditions for example, as required by external professional bodies or to improve the quality of the course.
Fees & financial support
Tuition fees
- 2024/25 entry: £2,360
Please note: the fees listed here are correct for the stated academic year only. For more detailed information about our course fees please see our fees and finance pages.
Financial support
There are lots of ways you can access additional financial support to help you fund your studies - both from UCA and from external sources. Discover what support you might qualify for please see our financial support information.
Additional course costs
In addition to the tuition fees there may be other costs for your course. The things that you are likely to need to budget for to get the most out of a creative arts education will include books, printing costs, occasional or optional study trips and/or project materials.
These costs will vary according to the nature of your project work and the individual choices that you make.
Course
Connections
This qualification is the final stage in training to become an architect and will leave graduates with the skills and competencies needed to become a professional architect. Graduates might go on to work in roles that include:
- Freelance architect
- Architectural rechnologist
- CAD technician
- Town planner
- Urban designer
- Interior & spatial designer
Entry requirements
Applicants should have a RIBA/ARB Part 1 and Part 2 in architecture or equivalent.
If your first language is not English a certificate is required as evidence that you have an average IELTS score of 6.0 or equivalent.
You may be offered a place on a course on the condition that you improve your English language and study skills. We offer pre-sessional English language courses which can improve your IELTS score by a maximum of 1.0 and 0.5, or equivalent.
Please Note:
Upon reaching the Part 3 oral examination, applicants should have recently completed a minimum of 24 months' practical experience under the direct supervision of a professional working in the construction industry. This should include at least 12 months working in the EEA, Channel Islands or the Isle of Man, under the direct supervision of an architect.
To gain access the ARB register one must obtain ARB/RIBA Part 1, Part 2 and Part 3.
